Maintenance of undercarriage components
The requirements for the maintenance of the components of the undercarriage systems are spelled out in the product passports and manuals for the operation of equipment. Compliance with the requirements influences the decision to recognize cases of breakdown or failure of spare parts as warranty.
The main indicators of the technical condition of the tracked equipment undercarriage include: track tension, wear of the track links, bushings and lugs of the track, wear of the teeth of the sprockets, wear of the running tracks of the guide wheels, track and support rollers, clearances in the bearing units of the system.
The technical condition of the undercarriage directly affects the performance of the equipment. So, if the tractor tracks are not properly tensioned, its movement requires up to 10% more power than usual, that is, less power remains for useful work. To prevent sudden failures, premature wear and misalignment, check the condition of the undercarriage components in a timely manner (in accordance with the maintenance intervals established by the manufacturer of the equipment) and, if necessary, repair the damage.
UNDERCARRIAGE MAINTENANCE INTERVALS
Recommended undercarriage maintenance intervals:
Per shift or every 10 hours:
-
Visual inspection of the undercarriage.
-
Cleaning from dirt, stones, spills, etc. Pay particular attention to track tension and blockage between links, bushings and shoe.
Every 50 hours or once a week:
-
Inspect pivot pins for grease and liquid lubricated pivot pins for hot pins and grease leaks.
Every 250 hours or once a month:
-
Measuring and adjusting the tension of the tracks.
-
Torque control and tightening of all shoe bolts.
Data on all detected malfunctions and the work carried out to eliminate them should be entered in the logbookl.
VISUAL INSPECTION OF THE UNDERCARRIAGE
1. Before starting work, the operator of the equipment should carry out a visual inspection of the tracks parts , track and support rollers, idler and sprockets, paying particular attention to the presence of possible signs of loosening the fastening bolts, especially shoe bolts. If loose bolts are found, they must be immediately tightened to the required tightening torque by the value indicated in the product passport or recommended in the equipment operation manual.
2. Inspect the support rollers, track rollers and idler for possible oil leaks. If the machine is equipped with grease or oil lubricated pivot tracks, check the tracks for possible leaks in the pivot area.
3. When moving at low speed around the site, listen for any squeaks, knocks or other abnormal noises.
4. If increased wear or oil leaks are found, it is necessary to carry out maintenance or repairs to restore the normal operation of the unit, or contact the service center for such maintenance or repair.
INSPECTION OF THE TRACK CHAIN JOINTS
1. During machine operation, the operator should listen to any unusual noises and squeaks. Thus, it is possible to identify in time joints in which there is no lubrication, or there are cracks and breakages in the shoes.
2. It is necessary to check the track joints for the presence of unlubricated alignments at least once every week. After stopping the machine, you can gently touch pins or bushings with the back of your hand, gloved.
If hinges are found that are too hot to the touch (above 50 ° C) it is necessary to mark these hinges.
3. An infrared thermometer can be used instead of the hand back. It should be noted those compounds whose temperature is too high (above 50 ° C).
4. If the number of marked pivots during the warranty period exceeds 10% of the total number of track links and traces of oil drips from the pivot are visible, contact the supplier of the track with a claim for pivot leaks to repair or replace the track.
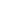
MEASURING AND ADJUSTING TRACTOR TRACK TENSION
Track slack over the carrier roller is a commonly used parameter to determine the amount of track tension.
-
In order to find out the amount of slacking A of the tracks of tractors with a traditional arrangement of the drive wheel (oval shape of the undercarriage), you need to put a straight bar (bar) on the lugs of the shoes, which are located between the support roller and the tension wheel and the tape measure, measure the gap between the surface of the bar and the lowest located grouser.
-
After obtaining the track slack size A, compare it with the value recommended by the tractor operating manual and adjust the tension if necessary.
To find out how much the track of a bulldozer with an upper drive wheel (triangular shape of the undercarriage) slacks, you need to pull the thread between the drive wheel and the front idler wheel and measure the distance between the thread and the top of the shoe lugs with a tape measure. The A value will represent the maximum track slack.
If the machine is equipped with a carrier roller, the average of dimensions B and C must be calculated.
In general, it is recommended (if this does not contradict the instructions in the maintenance instructions) that the amount of sagging of the track A is from L / 25 to L / 35, where L is the distance between the lugs of the shoes on which the bar lies.
MEASURING AND ADJUSTING EXCAVATOR TRACK TENSION
To determine the track tension of a hydraulic excavator, slowly raise the undercarriage with the boom and arm of the excavator, then, taking precautions in the event of a sudden undercarriage falling, measure the clearance between the bottom of the undercarriage and the top of the track shoe (distance A). Clearance B can be determined by measuring the distance between the track roller treadmills and the track chain. The distance A must be such that the clearance B is 60 to 100 mm for mini excavators and medium excavators, and 100 to 150 mm for large hydraulic excavators.
As a simplified version (without lifting the track bogie), you can measure the slacking of the track similarly to the measurement on a machine with an oval undercarriage, the recommended value should be from L / 35 to L / 50, where L is the distance between the lugs of the shoes on which the timber lies.
For correct tension, you need to compare the amount of slack with the amount recommended by the operation manual for a particular excavator model and adjust the tension if necessary.
MONITORING THE TIGHTENING TORQUE OF THE BOLTS
The loosening of the shoe bolts leads to breakage of both the bolts and the loss and breakage of the shoes, the impossibility of full restoration of the track due to the fact that the holes in the links and shoes become oval and an additional gap appears between them and the shoe bolts.
The tightening torque differs for shoe bolts of different standard sizes, when checking and tightening, it is necessary to observe the tightening torque recommended by the manufacturer for a specific standard size of the bolt thread.
When installing a new track on a machine, check the shoe bolt tightening torque every 10 hours during the first 60 hours of operation. Further checks of tightening torques should be carried out regularly in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations in the product passport and / or the operating experience by its operator, but at least after 250 hours, for tracks with liquid lubrication of the hinges - after 100 hours. When checking the tightening torque and tightening the shoe bolts, you must use a special torque wrench or multiplier set to the required torque. When tightening the bolts, the forces of rotation must be distributed evenly, without jerking. The bolts must be tightened according to the diagram shown in the figure (crosswise). As soon as the required torque value is reached, you need to stop tightening the bolts. Overtightening the bolt leads to an excess of the yield strength and elongation of the bolt body, which, in turn, leads to a weakening of the tightening torque and, subsequently, to bolt breakage.

 1 Mira Avenue, b. 4, Cheboksary, Chuvash Republic, Russia, 428003
1 Mira Avenue, b. 4, Cheboksary, Chuvash Republic, Russia, 428003